Agentic AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s fast becoming a foundational layer of enterprise automation. As companies move beyond basic chatbots and generative tools, they are increasingly turning to autonomous agents that can perceive goals, plan actions, invoke tools, and deliver outcomes with minimal oversight. This guide provides a strategic roadmap implementing Agentic AI—from early education to enterprise deployment—while highlighting the risks, architectural decisions, and organizational readiness required to succeed.
But for CTOs, CIOs, innovation leads, and functional heads, the question isn’t just “What is Agentic AI?” It’s:
How do we implement it responsibly, effectively, and at scale?
1. What Makes Agentic AI Strategic?
Agentic AI differs from traditional automation or generative AI in that it acts autonomously within complex environments. Rather than requiring manual prompts, agentic systems can:
- Interpret high-level goals (e.g., “Handle the client’s onboarding”)
- Create multi-step plans
- Execute those plans using APIs, tools, or documents
- Monitor success, self-correct, and learn
This moves AI from information assistance to true operational enablement.
Why it matters to leaders:
- Reduces manual intervention and bottlenecks
- Enhances responsiveness and personalization at scale
- Integrates with legacy and modern systems through APIs
- Drives intelligent workflows across departments
Related – Market Map for Agentic AI: Navigating Tools and Vendors
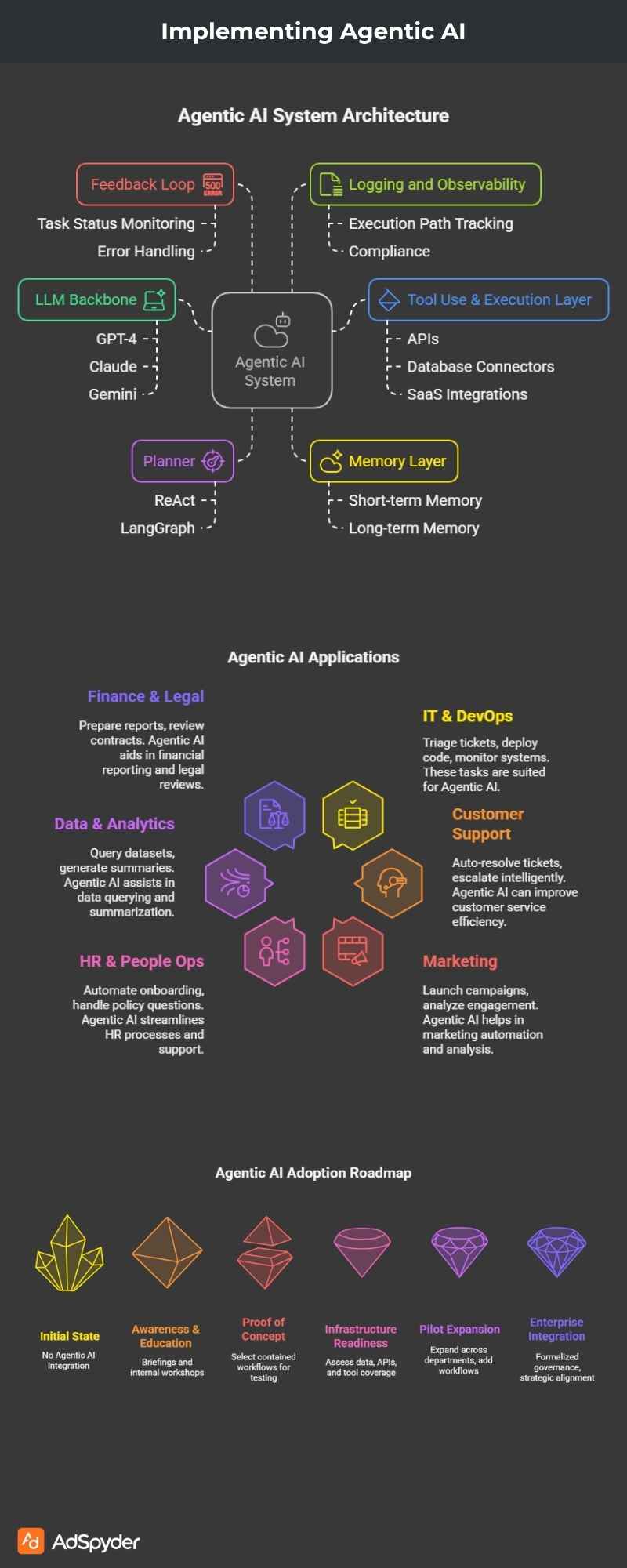
2. Where Are Enterprises Starting?
Based on market trends and early adopters, most organizations are exploring Agentic AI in these key areas:
| Function | Sample Use Cases |
| IT & DevOps | Triage tickets, deploy code, monitor systems |
| Customer Support | Auto-resolve tickets, escalate intelligently |
| Marketing | Launch campaigns, analyze engagement |
| HR & People Ops | Automate onboarding, handle policy questions |
| Data & Analytics | Query datasets, generate summaries |
| Finance & Legal | Prepare reports, review contracts |
These are domains where repetitive tasks + clear APIs + goal-driven workflows intersect—making them ideal for early adoption.
3. Key Components of an Agentic AI System
To build or deploy agentic AI, organizations need to understand its modular architecture:
a. LLM Backbone
The reasoning engine (e.g., GPT-4, Claude, Gemini) that interprets instructions, generates plans, and makes decisions.
b. Planner
Breaks down goals into actionable steps using structured logic (e.g., ReAct, LangGraph).
c. Memory Layer
Stores context across steps or sessions—both short-term (local memory) and long-term (vector stores).
d. Tool Use & Execution Layer
APIs, database connectors, SaaS integrations, internal scripts, RPA bots, and more.
e. Feedback Loop
Monitors task status, checks for errors, retries or escalates as needed.
f. Logging and Observability
Tracks execution paths for transparency, debugging, and compliance.
This modular approach allows teams to start small and scale incrementally, integrating existing systems and gradually expanding autonomy.
Check Out – Top Agentic AI Tools for 2026
4. Strategic Roadmap for Adoption
Implementing Agentic AI isn’t a one-step rollout. Here’s a phased approach enterprises can follow:
Phase 1: Awareness & Education
- Executive briefings on agentic vs generative AI
- Internal workshops for tech and business teams
- Pilot projects identified based on task complexity and data/API availability
Phase 2: Proof of Concept
- Select 1–2 contained workflows (e.g., support ticket triage)
- Use open-source tools (e.g., LangChain, CrewAI) or agent-as-a-service platforms
- Define success metrics (cost/time savings, resolution accuracy)
Phase 3: Infrastructure Readiness
- Assess data accessibility, API maturity, and tool coverage
- Set up logging, monitoring, and guardrails
- Prepare DevOps pipelines for agent deployment
Phase 4: Pilot Expansion
- Expand across departments or to external-facing use cases
- Add multi-agent workflows (e.g., cross-team coordination)
- Introduce human-in-the-loop mechanisms for edge cases
Phase 5: Enterprise Integration
- Formalize governance (AIOps, AI safety, audit trails)
- Align with strategic goals (e.g., reducing ticket backlog by 40%)
- Enable self-serve platforms for teams to deploy and manage agents
5. Organizational Alignment: Getting Buy-In Across Stakeholders
Implementing Agentic AI isn’t just a technical shift—it’s an operational and cultural one. Success depends on clear alignment across roles.
a. Executive Leadership (C-suite)
- Define vision: Align agentic AI with strategic priorities (efficiency, innovation, customer experience).
- Provide sponsorship and funding.
- Understand the difference between automation, chatbots, and agents.
b. Tech Leadership (CTO, CIO, Heads of AI)
- Identify integration opportunities in the tech stack.
- Select agentic frameworks and LLM partners.
- Balance innovation with maintainability and governance.
c. Functional Leaders (Ops, HR, Marketing, Support)
- Provide workflow expertise for agent training.
- Identify pain points that agents can address.
- Own success metrics like turnaround time, accuracy, or employee productivity.
d. AI/ML Teams & Developers
- Build, test, and deploy agents using toolkits like LangChain or LangGraph.
- Define input/output boundaries, memory usage, and retry logic.
- Monitor and retrain agents as systems evolve.
e. Legal, Compliance, and Risk
- Review data access, auditability, and agent behavior.
- Define acceptable risk thresholds and fail-safe triggers.
- Ensure alignment with data privacy and governance policies.
Recommended For You – Agentic AI Frameworks for Teams
6. Key Risks and How to Mitigate Them
As with any transformative technology, Agentic AI comes with trade-offs and potential risks.
a. Uncontrolled Execution
- Risk: An agent calls external APIs or executes commands incorrectly.
- Mitigation: Use guardrails, simulation modes, human-in-the-loop validation, and execution whitelists.
b. Lack of Observability
- Risk: Teams don’t understand what the agent is doing.
- Mitigation: Use tools like LangSmith or OpenTelemetry for logging and traceability.
c. Over-reliance on LLM Behavior
- Risk: Prompt variability causes inconsistent outputs.
- Mitigation: Combine LLM reasoning with deterministic checks and tool-based constraints.
d. Data Privacy Concerns
- Risk: Agents access sensitive or regulated data.
- Mitigation: Enforce access controls, pseudonymization, and in-memory execution where possible.
e. Organizational Resistance
- Risk: Teams resist agentic systems due to fear of job loss or confusion.
- Mitigation: Educate stakeholders, highlight augmentation vs. replacement, and involve users in agent design.
7. Strategic Questions to Guide Adoption
Before scaling Agentic AI, leaders should ask:
- Which business processes are goal-driven, repetitive, and high-volume?
- Do we have the necessary APIs and data pipelines to support agent decisions?
- How will we monitor agent behavior and output?
- Who owns the success metrics for each deployment?
- Are we positioned to support cross-functional workflows with agentic logic?
- Do we need enterprise-grade tooling or can we start with open frameworks?
These questions help organizations prioritize wisely, avoiding tech-for-tech’s-sake deployments.
8. Build vs Buy: Choosing the Right Deployment Path
When implementing agentic AI, organizations often face a key decision:
Should we build internally or adopt third-party solutions?
a. Build In-House
- Use when: You have a strong internal AI/engineering team, need deep customization, or wish to control intellectual property.
- Tools: LangChain, LangGraph, CrewAI, AutoGen, custom APIs.
- Benefits: Full control, flexibility, data ownership.
- Challenges: Higher maintenance, requires internal AI literacy.
b. Buy or Subscribe to SaaS Agentic Platforms
- Use when: You want faster time-to-value or have domain-specific workflows (e.g., HR, IT, marketing).
- Vendors: Aisera (support), Cognosys (dev), Adept (automation), Dust (knowledge work).
- Benefits: Rapid deployment, domain expertise, integrated tooling.
- Challenges: May have limits on customization or data handling.
c. Hybrid Strategy
- Most enterprises will mix both—buy for standard workflows and build for strategic IP-driven initiatives.
9. Success Metrics and KPIs
To track the ROI and effectiveness of agentic AI deployments, monitor:
| KPI | Relevance |
| Task Completion Rate | Measures the functional reliability of agents |
| Average Handling Time (AHT) | Tracks speed improvement vs. manual workflows |
| Escalation Frequency | Gauges when agents need human support |
| Cost per Resolution/Action | Useful for comparing against manual ops |
| User Satisfaction (CSAT/NPS) | Measures end-user experience with agent output |
| Failure Recovery Time | Indicates agent resilience and retry quality |
Regular reviews against these metrics help ensure agentic systems remain aligned with business goals.
Final Thoughts: Strategic Alignment Over Hype
Agentic AI is not a silver bullet. But it is one of the most promising paradigms for modern enterprise automation—especially as organizations seek ways to reduce complexity, empower teams, and respond faster to business needs.
The most successful implementations will come from companies that:
- Start with a clear goal, not a tool
- Think in systems, not features
- Invest in people as much as platforms
- Embrace experimentation with guardrails
By aligning technical architecture with strategic objectives, and adopting agentic AI with intent—not impulse—organizations can lead, not lag, in the next era of enterprise intelligence.
FAQs
What is Agentic AI and why does it matter for enterprises?
Agentic AI enables autonomous task execution through goal understanding, planning, memory, and tool usage. It moves beyond conversational AI and helps automate complex workflows end-to-end.
How is Agentic AI different from traditional automation or RPA?
Traditional automation follows fixed rules or scripts. Agentic AI dynamically plans and executes tasks using reasoning, language models, and tool orchestration, adapting to context in real time.
Where should enterprises start with Agentic AI?
Begin with use cases that are repetitive, API-accessible, and high volume—like IT support, onboarding, marketing automation, or customer queries.
What technical components are required for Agentic AI systems?
A typical system includes a large language model (LLM), planning engine, memory, tool/API interfaces, execution controller, and observability/logging tools.
Should we build our own agents or buy SaaS platforms?
It depends. Build in-house for proprietary workflows or deeper customization. Buy platforms when speed, usability, and integration are priorities. A hybrid model often works best.
What are the major risks of implementing Agentic AI?
Risks include uncontrolled actions, data exposure, lack of visibility into decisions, and system brittleness. These can be mitigated with strong governance, logging, and human-in-the-loop systems.
Do we need a dedicated AI team to implement agentic systems?
Not always, but it helps. Agentic AI requires collaboration across engineering, product, security, and operations. AI expertise is important for prompt design, LLM tuning, and orchestration.
What KPIs should we track to evaluate success?
Monitor task completion rate, average handling time, cost per task, escalation frequency, and satisfaction scores from users or customers.
How do we get executive buy-in for Agentic AI?
Tie projects to business outcomes like faster resolution times, lower cost-per-action, or reduced manual workload. Present it as strategic automation, not experimental tech.
How fast can we go from pilot to scale?
Pilot cycles can take 4–8 weeks. Scaling depends on use case complexity, system maturity, and readiness of data/tools. Most organizations scale gradually across functions.