Dropshipping has become one of the most accessible ways to launch an ecommerce business in today’s digital economy. With no inventory to stock, no warehouses to manage, and minimal upfront costs, the model is perfect for entrepreneurs who want to start lean and scale quickly.
But while dropshipping seems simple on the surface, building a profitable store requires strategy, the right tools, supplier relationships, and marketing knowledge for handling supply-chain, shipping, and customer challenges that inevitably arise.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about dropshipping — how it works, different models, how to start, how to market your store, how to scale, and how to avoid common mistakes.
What Is Dropshipping & Why People Choose It
Dropshipping is an ecommerce fulfillment model where the online store sells products without holding any inventory. Instead:
-
A customer buys a product from your online store.
-
You forward the order to your supplier.
-
The supplier packages and ships the product directly to the customer.
You earn the profit between the retail price and the supplier cost.
Why dropshipping remains popular:
-
No upfront inventory
-
Low financial risk
-
Easy to launch
-
Wide product variety
-
Fast testing of new niches
-
Can scale with minimal resources
It’s perfect for creators, new entrepreneurs, or marketers skilled in performance ads, influencer campaigns, or paid pragmatic marketing approaches.
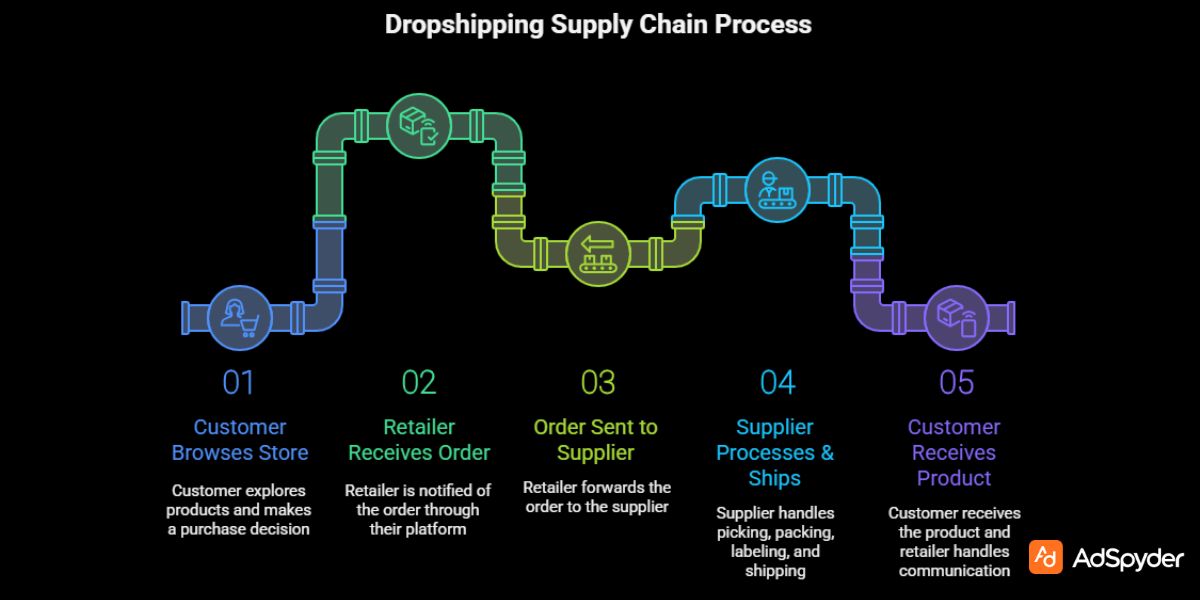
How Dropshipping Works — The Entire Fulfillment Flow
Dropshipping relies on a simple but well-defined supply chain:
1. Customer Browses Your Store
They explore products, read descriptions, compare variants, and make a purchase decision.
2. Retailer (You) Receives the Order
The store notifies you automatically through Shopify, WooCommerce, or your ecommerce platform.
3. Order Sent to Supplier
You forward the order to a supplier via:
-
AliExpress
-
DSers
-
Spocket
-
CJDropshipping
-
Print-on-Demand providers
4. Supplier Processes & Ships
The supplier handles:
-
Picking
-
Packing
-
Labeling
-
Shipping
-
Tracking numbers
5. Customer Receives the Product
You remain the face of the brand responsible for communication, service, returns, and policy enforcement.
Because you don’t manage inventory or logistics, you can focus on marketing, scaling, content, and optimizing your b2b video marketing funnel or consumer-facing campaign funnels depending on the niche.
Types of Dropshipping Models You Can Use
Different dropshipping structures fit different business goals. Here’s an expanded look at each model:
1. Traditional International Dropshipping
You source products from global suppliers, usually in China or Southeast Asia.
Pros:
-
Low costs
-
Large catalog
-
Easy to test trending products
Cons:
-
Long shipping times
-
Language and communication barriers
-
Higher return risks
This model often benefits from strong ad creative testing using tools like AdSpyder’s facebook ads spy tool to analyze competitors’ creatives.
2. Print-on-Demand (POD) Dropshipping
Products are only printed after purchase (T-shirts, bags, posters, accessories).
Pros:
-
Zero inventory
-
Strong brand identity
-
High perceived value
Cons:
-
Higher per-unit cost
-
Limited categories
This model is ideal for creators or niche brands wanting unique designs.
3. Domestic / Local Dropshipping
Suppliers are located within your country.
Pros:
-
Fast delivery
-
Easier customer satisfaction
-
Better return handling
Cons:
-
Higher product cost
-
Smaller supplier network
A strong option for niches like home improvement, fitness, and even real estate advertising merchandise (signage, printables, branded materials).
4. Niche Dropshipping
You specialize in a specific category, building brand loyalty and authority.
Examples:
-
Pet grooming tools
-
Eco-friendly kitchen essentials
-
Automotive accessories
-
Home fitness equipment
Pros:
-
Easier branding
-
Repeat customers
-
Less competition than general stores
Cons:
-
Requires research to validate demand
5. Hybrid Dropshipping
You stock top performers yourself and dropship the rest.
Pros:
-
Faster shipping for best-sellers
-
Better control of packaging and quality
Cons:
-
Some upfront investment required
Useful for stores scaling from dropshipping to a branded ecommerce model.
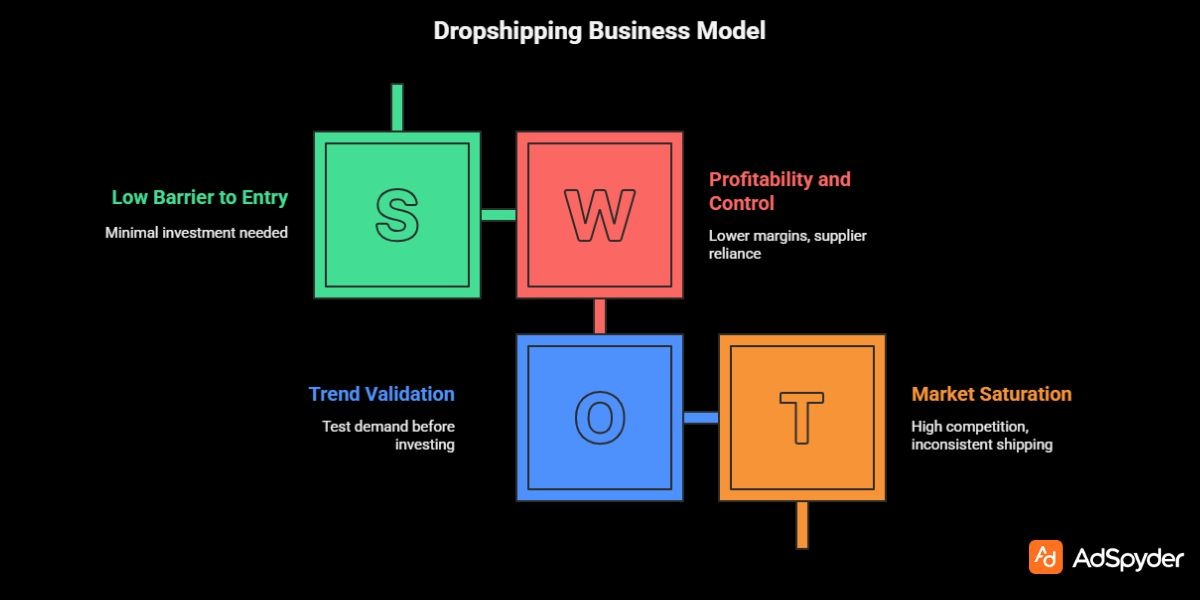
Pros & Cons of Dropshipping — A Balanced View
To succeed, entrepreneurs must understand the realities of this business model.
Pros
1. Minimal Startup Cost
No warehouse, inventory, or bulk purchases needed.
2. Easy Product Testing
Perfect for trend testing or validating demand before investing.
3. Wide Product Selection
Sell hundreds of items without managing logistics.
4. Flexible & Scalable
Operate from anywhere with internet access.
5. Low Operational Complexity
Suppliers manage inventory and shipping.
Cons
1. Lower Profit Margins
You pay retail-friendly wholesale prices.
2. Supplier Reliance
Delays, quality issues, or mispackaged orders affect your brand — requiring strong crisis management strategies.
3. Higher Competition
Many stores use similar suppliers.
4. Shipping Inconsistency
International delivery times vary widely.
5. Difficult Returns
You must coordinate between customers and suppliers, which can be messy.
How to Start a Dropshipping Business — Step-by-Step Guide
This section expands on each step with deeper, actionable insights.
1. Choose a Niche That Can Be Profitable
Pick a niche with:
-
Passionate audiences
-
Evergreen demand
-
Low return rates
-
Strong upsell potential
Examples:
-
Home fitness gear
-
Pet care tools
-
Beauty gadgets
-
Hobby tools
Avoid niches with:
-
High breakage rates
-
Legal complications
-
Extremely heavy items
2. Find Reliable Suppliers
Your supplier determines your store’s success rate.
Supplier evaluation checklist:
-
Product quality (order samples)
-
Shipping insurance
-
Refund policies
-
Inventory stability
-
Communication response time
-
Real customer reviews
Always keep 2–3 backups so operations never halt.
3. Build Your Ecommerce Store
Choose a platform like Shopify, WooCommerce, or Wix.
Essential elements to include:
-
Compelling homepage hero section
-
Clean navigation structure
-
Category pages with SEO-rich content
-
Mobile-optimized product pages
-
Trust badges and social proof
-
Simple checkout
Add analytics tools to track behavior and funnel progression.
4. Select Products & Set Data-Backed Pricing
Price your products based on:
-
Supplier cost
-
Market competition
-
Product uniqueness
-
Shipping cost
-
Target profit margin
Your pricing strategy should leave room for discount codes and paid ads.
5. Set Up Logistics, Customer Policies & Automation
Even when suppliers handle fulfillment, you must define:
-
Shipping transparency
-
Return/refund process
-
Warranty expectations
-
Customer service scripts
Automation tools streamline:
-
Order routing
-
Tracking notifications
-
Email flows
-
Upsell suggestions
6. Launch Marketing Campaigns
Dropshipping success is driven by consistent traffic generation.
Best traffic channels:
-
TikTok ads
-
Facebook/Instagram ads
-
Google Shopping
-
Influencer collaborations
-
SEO
-
Email marketing
Paid ads paired with creative testing and paid marketing strategies help you scale quickly.
7. Track Performance & Scale What Works
Monitor:
-
Conversion rate
-
Add-to-cart rate
-
Average order value
-
ROAS (Return on Ad Spend)
-
Customer lifetime value
Expand winning products, kill underperformers, and scale channels methodically.
SEO & Store Optimization for Dropshipping
SEO is essential for reducing ad dependency and building long-term organic traffic.
1. Write Unique Product Descriptions
Avoid using supplier-provided descriptions.
Your content should:
-
Focus on benefits
-
Tell a compelling product story
-
Include keywords naturally
2. Optimize Site Structure
Use a flat architecture:
Home → Category → Subcategory → Product
It helps both Google and shoppers navigate easily.
3. Use Long-Tail Keywords
Target keywords like:
-
“best dropshipping fitness tools for beginners”
-
“eco-friendly household dropshipping products”
-
“pet grooming tools under $30”
These convert much better than generic keywords.
4. Improve Technical SEO
Focus on:
-
Faster page load
-
Mobile UX
-
Image compression
-
Schema markup
Dropshipping sites often have many images, so optimizing load speed is crucial.
5. Build Helpful Content
Blog topics can include:
-
Product comparison guides
-
Niche-specific tips
-
Industry insights
-
Seasonal buying guides
A strong blog helps you rank for information-focused keywords.
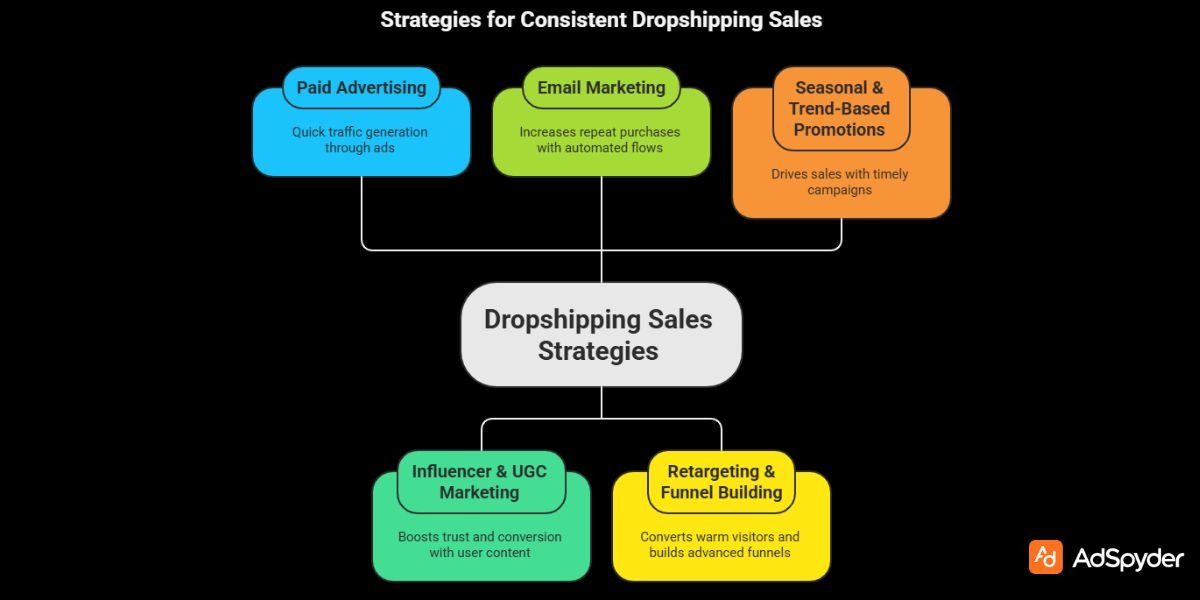
Marketing Strategies Beyond SEO — How to Drive Growth
Here are proven ways dropshipping brands generate sales consistently.
1. Paid Advertising
The quickest way to get traffic.
Use:
-
Facebook & Instagram ads
-
TikTok ads
-
Google Shopping ads
Use an ads spy tool like AdSpyder to analyze competitor creatives, hooks, and copy angles.
2. Influencer & UGC Marketing
User-generated content drastically boosts trust and conversion.
Encourage influencers to film:
-
Product unboxings
-
Tutorials
-
Before/after results
-
Lifestyle content
Short-form video ads typically outperform image ads.
3. Email Marketing
Set up automated flows:
-
Welcome emails
-
Abandoned cart recovery
-
Post-purchase upsells
-
Product recommendation sequences
Email increases repeat purchase rates significantly.
4. Retargeting & Funnel Building
Retargeting helps convert warm visitors who didn’t buy.
You can also build a more advanced b2b video marketing funnel if you’re selling dropshipping services, not physical goods.
5. Seasonal & Trend-Based Promotions
Run campaigns during:
-
Back to school
-
Holidays
-
Summer/winter essentials
-
Major sale events
React quickly to viral trends for fast conversion spikes.
Common Dropshipping Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Avoid these pitfalls that kill most beginner stores.
1. Selling Generic, Over-Saturated Products
Add branding, bundles, or unique positioning to stand out.
2. Working With Only One Supplier
Redundancy keeps your business stable.
3. Ignoring Customer Service
Slow responses lead to chargebacks and bad reviews.
4. Overcomplicating the Store
Simpler stores convert better.
5. No Crisis Playbook
Shipping delays, supplier issues, and lost packages require crisis management strategies for fast resolution.
Quick Launch Checklist
Use this before going live:
-
Niche validated
-
Suppliers tested
-
Unique product descriptions written
-
Paid and organic marketing strategy mapped
-
Policies and automation in place
-
Tracking installed (GA4, pixel, etc.)
-
Retargeting enabled
FAQs
Is dropshipping still profitable?
Yes — when paired with smart product selection and strong marketing execution.
How much do I need to start?
Most start with $100–$500, mainly for ads and basic tools.
Do I need to stock any products?
No — suppliers handle inventory and shipping.
What niches work best?
Fitness, beauty, pet care, kitchen essentials, and hobby-based niches.
Are shipping delays common?
Yes for international suppliers — communicate transparently to customers.
Is dropshipping legal?
Yes, as long as you follow consumer laws and supplier terms.
Can I turn dropshipping into a full-time business?
Many entrepreneurs do — after scaling ads, optimizing SEO, and building brand loyal customers.
Conclusion — Is Dropshipping Right for You?
Dropshipping offers a low-risk, flexible, and scalable path into ecommerce. Whether you’re a beginner testing your first online store, a marketer running paid marketing campaigns, or an entrepreneur transitioning into private labeling, dropshipping provides the foundation to learn, grow, and build a sustainable online business.
Success doesn’t come from listing hundreds of products — it comes from smart research, supplier trust, strong branding, and relentless optimization.
If you’re ready to start a business with low upfront investment and huge potential, dropshipping is still one of the best models to get started.