As conversational interfaces become common in customer service, HR, healthcare, and enterprise workflows, one key question arises:
What’s the difference between an Agentic AI vs Chatbots?
They may seem similar on the surface—both take user input and respond—but their capabilities, architecture, and impact are dramatically different.
In this post, we’ll explore how traditional chatbots differ from agentic systems, and why more organizations are transitioning from simple bots to autonomous agents.
What Is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a program that simulates conversation with users through text or voice interactions. Chatbots can be:
- Rule-based: Follow decision trees and keyword triggers.
- AI-powered: Use NLP and machine learning to understand intent and respond.
They’re often used for:
- FAQs and helpdesk support
- Lead qualification
- Scheduling and booking
- Feedback collection
Despite advances in language understanding, most chatbots remain reactive—they provide information but do not independently plan or take action.
Related – Agentic AI vs AI Agents
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a newer system design built on large language models (LLMs), enhanced with:
- Goal interpretation
- Multi-step planning
- Dynamic tool usage
- Memory and context management
- Feedback loops and self-refinement
Unlike a chatbot that waits for input and responds within a script, an agentic AI system can understand a goal and autonomously complete a task—often across multiple tools and steps.
Core Differences at a Glance
| Capability | Chatbot | Agentic AI |
| Input Type | Text or voice | Natural language (text) |
| Output Type | Response | Response + action |
| Planning | Pre-scripted or none | Dynamic, multi-step planning |
| Tool/API Use | Limited or static | Dynamic and context-aware |
| Autonomy | Reactive | Goal-driven and proactive |
| Memory | Stateless or session-limited | Stateful (short-term + persistent memory) |
| Execution | Text replies only | Executes tasks via API, scripts, or agents |
Example Scenario: Customer Service Refund Request
User Input:
“I want to cancel my subscription and get a refund for this month.”
Chatbot Response:
“I’m sorry to hear that. Please visit [link] to cancel. Our refund policy is…”
Agentic AI Response and Action:
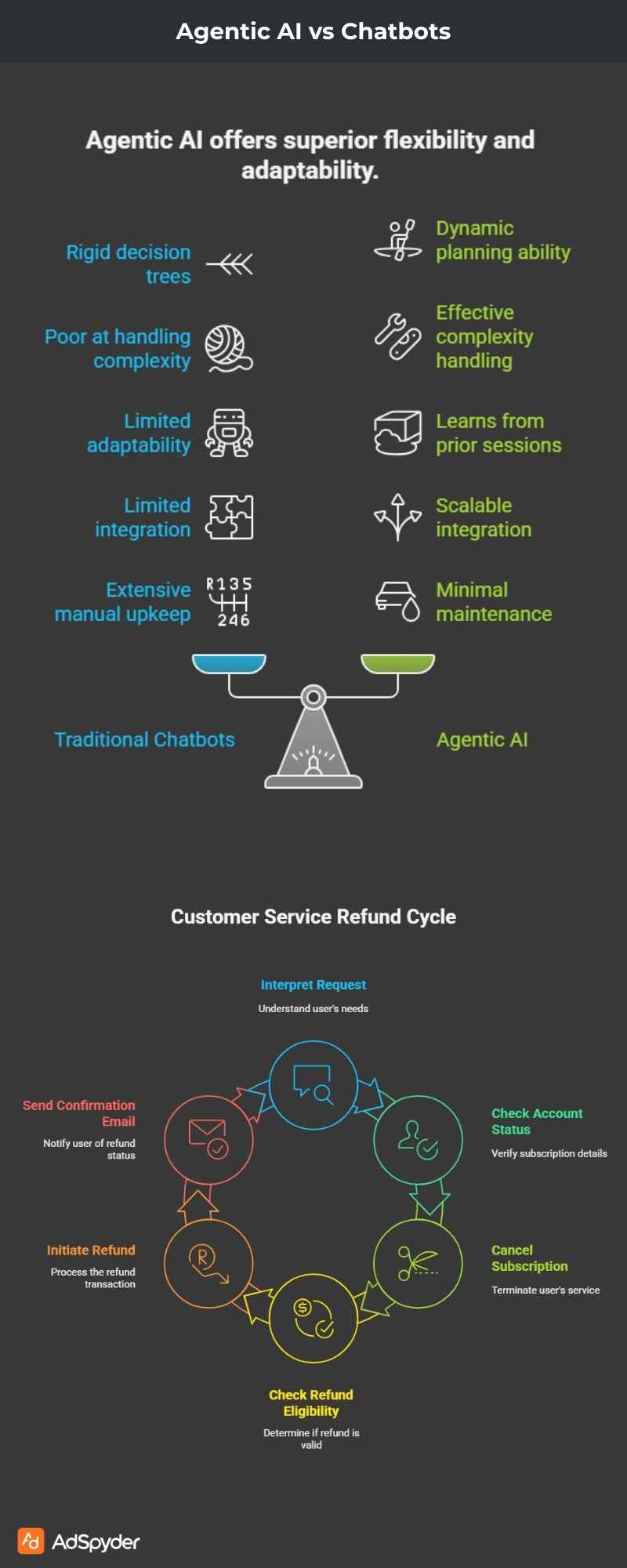
- Interprets the request and checks account status
- Cancels the subscription using internal APIs
- Checks refund eligibility
- Initiates refund if valid
- Sends confirmation email with support contact
Agentic AI handles the entire task autonomously, not just the conversation.
Check Out – Agentic AI vs RAG
Limitations of Traditional Chatbots
- Rigid decision trees
- Poor at handling ambiguous or complex requests
- Can’t adapt to changing user goals mid-session
- Limited integration with external systems
- Require extensive manual configuration and upkeep
In contrast, Agentic AI can:
- Dynamically plan based on context
- Choose the best tool or API to invoke
- Learn from prior sessions or examples
- Scale across domains without retraining
Check Out – Agentic AI vs AGI
Use Case Comparison
| Use Case | Best Fit |
| Answering FAQs | Chatbot |
| Booking a table from user input | Chatbot |
| Analyzing and routing IT support | Agentic AI |
| Managing customer subscriptions | Agentic AI |
| Escalating HR issues with reasoning | Agentic AI |
| Collecting contact information | Chatbot |
When Does a Chatbot Become an Agent?
A chatbot becomes “agentic” when it can:
- Go beyond dialogue to take meaningful, independent action
- Select and use external tools or APIs
- Modify its plan based on feedback or new information
- Maintain and use memory to personalize or adapt behavior
The transition isn’t just technical—it reflects a shift from interface to intelligent automation.
Final Thoughts for Agentic AI vs Chatbots
Chatbots introduced us to conversational interfaces. But as enterprise needs move beyond scripted interactions to real-time, dynamic task resolution, the limitations of traditional bots become clear.
Agentic AI offers a smarter, more scalable future—where systems don’t just talk, they think and act.
If chatbots were version 1.0 of interactive AI, agentic systems represent the leap to 3.0: intelligent, autonomous, and outcome-oriented.
Must See – Agentic AI Market Map
FAQs for Agentic AI vs Chatbots
How is a chatbot different from Agentic AI?
Chatbots mainly reply to user messages using prewritten scripts or model-trained responses. Whereas Agentic AI can understand goals, make plans, and carry out tasks on its own—often using tools and logical reasoning. Chatbots are easy to implement, whereas Agentic AI requires more effort.
Is it possible for a chatbot to become agentic?
It can be—if you give it the ability to plan, remember past interactions, use tools, and make decisions without constant guidance. Without these, it’s just a conversational interface.
Do chatbots make use of large language models?
Not necessarily. Modern chatbots might rely on LLMs for better language handling. But they typically don’t have the broader planning or tool-handling abilities of an agentic AI system.
Can Agentic AI chat like a regular chatbot?
Absolutely—and it can go even beyond that. It can hold a natural conversation while also carrying out actions like booking appointments, updating data, or making choices based on what’s being said.
What are the weak points of traditional chatbots?
They’re mostly reactive. They stick to predefined scripts and don’t recall past conversations. They also can’t act on their own outside of replying to messages.
Is building Agentic AI more challenging than creating a chatbot?
Yes. It requires more advanced components, such as language models, planning systems, memory, and the ability to work with external tools. But it also offers much greater adaptability and usefulness.
When should I stick with a chatbot instead of Agentic AI?
If your needs are basic, a chatbot is enough. It can be like answering FAQs, guiding users through forms, or handling straightforward decision trees. For more complex, changing tasks, Agentic AI is the better fit.
Is Agentic AI more suited for business use?
Definitely. It’s especially valuable in enterprise environments where tasks involve multiple steps, tools, or teams—like customer support, HR processes, or IT workflows. These repititve tasks can be handled easily.
Can an existing chatbot be turned into Agentic AI?
Yes, you can do that, but with some effort. You’ll need to add features like reasoning, memory, planning capabilities, and tool usage.
Does Agentic AI still require user input?
Yes. But the key difference is, once it understands what needs to be done, it can move forward on its own without needing instructions at every step.