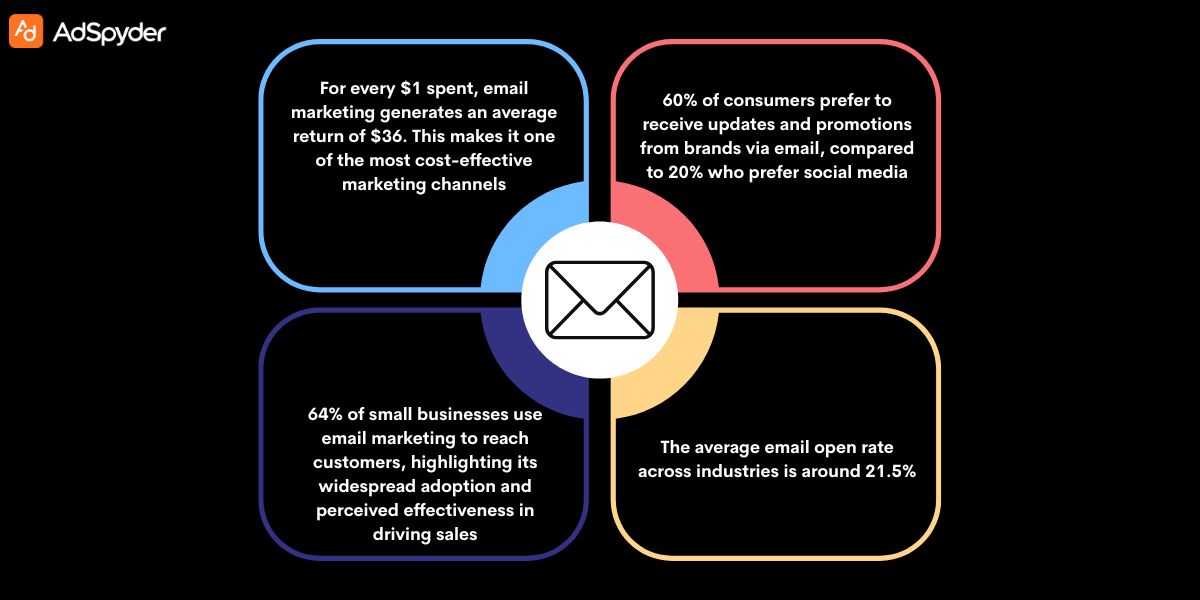
Among all digital marketing strategies, email marketing stands out as both highly impactful and cost-efficient. Whether you’re running email marketing for small businesses, managing campaigns for large enterprises, or growing a personal brand, a structured email marketing plan is what separates inconsistent results from predictable growth.
An email marketing plan gives you clarity on:
-
Who you’re targeting
-
What content you’ll send
-
When you’ll send it
-
Why each email exists
-
How you’ll measure success
Without a plan, most email campaigns become scattered, reactive, and underperforming. With a strategy, email becomes one of your strongest revenue and relationship-building tools.
Why You Need an Email Marketing Plan
An email marketing plan is your documented roadmap for using email to achieve specific business goals—sales, retention, awareness, onboarding, or engagement.
Without a clear plan, brands often:
-
Send emails inconsistently
-
Promote too often without adding value
-
Target the wrong audience segments
-
Ignore performance data
-
Burn out their email list
With a proper plan, you gain:
-
Consistency – predictable communication builds trust
-
Relevance – the right message reaches the right audience
-
Efficiency – automation saves time and manual effort
-
Higher ROI – email consistently outperforms many paid channels
This applies equally to email marketing for restaurants, service companies, ecommerce stores, and content creators.
Core Components of an Email Marketing Plan
Every successful email strategy is built on four pillars:
-
Goals and KPIs
-
List building and consent
-
Segmentation and audience personas
-
Content strategy and scheduling
Let’s break each one down.
1. Define Your Goals & KPIs
Your goals shape every decision you make in email marketing. Examples include:
-
Increasing online sales
-
Driving foot traffic for local businesses
-
Booking more demos or consultations
-
Growing blog readership
-
Upselling existing customers
-
Increasing repeat purchases
Once goals are defined, assign clear KPIs:
-
Open rate
-
Click-through rate (CTR)
-
Conversion rate
-
Revenue per campaign
-
Unsubscribe rate
-
List growth rate
For example:
-
Email marketing for IT services often focuses on demo bookings and consultation inquiries.
-
Email marketing for restaurants often prioritizes reservations and daily offer redemptions.
2. Build & Grow Your Email List the Right Way
Your email list is undoubtedly an asset. But growth must be permission-based and intentional.
Proven list-building methods:
-
Website sign-up forms
-
Exit-intent popups
-
Discount offers
-
Downloadable guides and checklists
-
Event registrations
-
Loyalty programs
Never buy email lists. That practice damages deliverability, reputation, and long-term performance—especially when using bulk email advertising, where reputation matters even more.
3. Segment Your Audience & Create Personas
Segmentation ensures relevance. Instead of sending one email to everyone, you send tailored content to smaller groups.
Common segmentation criteria:
-
New vs returning subscribers
-
Buyers vs non-buyers
-
Active vs inactive users
-
Location
-
Industry
-
Interests
-
Past behavior
This is crucial for:
-
Email marketing for bloggers, where content interests vary widely
-
Email marketing for small businesses, where customer intent differs based on purchase history
Personas make your emails feel human instead of generic.
4. Build a Content Strategy & Email Calendar
Your email marketing plan should clearly define:
-
What topics you’ll cover
-
How often you’ll email
-
What balance you’ll maintain between promotion and value
Common email content categories:
-
Educational
-
Promotional
-
Community-driven
-
Product updates
-
Events and announcements
Create a simple monthly or quarterly calendar listing:
-
Campaign name
-
Target segment
-
Objective
-
Content theme
-
Send date
This eliminates guesswork and ensures consistency.
Types of Emails & When to Use Them
A high-performing email system includes multiple types of emails working together.
1. Welcome & Onboarding Emails
These are triggered immediately after someone joins your list.
Purpose:
-
Introduce your brand
-
Set expectations
-
Deliver promised incentive
-
Guide next steps
For service brands and email marketing for small businesses, onboarding emails often educate subscribers on solutions, use cases, and case studies.
2. Newsletters & Content Updates
These build long-term engagement through:
-
Blog updates
-
Educational content
-
Industry insights
-
Success stories
-
Community news
This format works especially well for email marketing for bloggers, where audience trust is built on consistent value delivery.
3. Promotional & Sales Emails
These emails drive revenue through:
-
Limited-time offers
-
Seasonal sales
-
Product launches
-
Bundled promotions
They work best when balanced with value-driven emails so subscribers don’t feel constantly sold to.
4. Abandoned Cart & Behavioral Follow-Ups
Triggered based on:
-
Cart abandonment
-
Product views
-
Trial signups
-
Demo requests
These emails recover lost revenue and nurture warmer prospects automatically.
5. Re-Engagement & Win-Back Emails
Sent to inactive subscribers to:
-
Reignite interest
-
Offer incentives
-
Clean the list if needed
Essential for maintaining high deliverability.
6. Transactional & Lifecycle Emails
Includes:
-
Order confirmations
-
Shipping updates
-
Account alerts
-
Renewals
-
Subscription updates
These often have the highest open rates and should include subtle brand reinforcement.
Design & Deliverability Best Practices
Your strategy fails if your emails don’t reach inboxes or don’t look professional.
1. Standard Email Structure
Every email should include:
-
Subject line
-
Preheader text
-
Clear headline
-
Concise body copy
-
One primary CTA
-
Branded footer with unsubscribe
2. Mobile-First Design
Most users read emails on phones. Use:
-
Single-column layouts
-
Large tap-friendly buttons
-
Short paragraphs
-
High contrast text
3. Smart Personalization
Beyond first names, use:
-
Behavioral triggers
-
Purchase history
-
Browsing activity
-
Location-based offers
This boosts relevance and conversions dramatically.
4. Compliance & Trust Signals
Always include:
-
Clear unsubscribe
-
Physical business address
-
Honest subject lines
-
Opt-in confirmation
This protects both your sender reputation and brand trust.
5. Deliverability Optimization
To avoid spam filters:
-
Warm up domains gradually
-
Avoid spam trigger words
-
Maintain clean lists
-
Use proper domain authentication
-
Maintain consistent sending patterns
This is especially critical when running bulk email advertising campaigns at scale.
Automation & Workflow Setup
Automation allows your email marketing plan to scale without additional manual effort.
1. Choose the Right Email Platform
Look for:
-
Visual automation builder
-
Advanced segmentation
-
CRM integration
-
A/B testing
-
Behavior-based triggers
2. Core Automation Flows to Build First
Every email plan should include:
-
Welcome sequence
-
Abandoned cart flow
-
Post-purchase follow-ups
-
Lead nurture series
-
Re-engagement flow
3. Drip vs Triggered Campaigns
-
Drip sequences: Timed educational or onboarding series
-
Triggered emails: Activated by user behavior in real time
Both should exist in a complete email ecosystem.
4. Data-Driven Automation Optimization
Refine workflows based on:
-
Engagement drop-off
-
Conversion points
-
Heatmaps
-
Click behavior
-
Response timing
Automation should evolve as your audience evolves.
Email Marketing Plan – Metrics & Performance Tracking
A strong plan is nothing without continuous measurement.
Key Metrics to Monitor
-
Open rate
-
Click-through rate
-
Conversion rate
-
Revenue per email
-
Bounce rate
-
Spam complaints
-
List growth
-
Engagement by segment
How to Use These Metrics
Use performance data to:
-
Improve subject lines
-
Refine content topics
-
Adjust sending times
-
Enhance segmentation
-
Improve automation logic
Common Email Marketing Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
-
Sending generic messages to everyone
-
Over-emailing subscribers
-
Ignoring mobile optimization
-
Poor subject lines
-
Weak calls-to-action
-
Neglecting re-engagement campaigns
-
Failing to clean inactive subscribers
Avoiding these mistakes alone can double your results without increasing your email volume.
Sample Email Marketing Plan Template
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
| Goal | Increase online sales by 25% in 6 months |
| Segments | New leads, repeat buyers, inactive users |
| Email Types | Welcome, newsletters, promos, abandoned cart |
| Send Frequency | Weekly newsletters + automated flows |
| Tools | Email platform + CRM |
| KPIs | Open rate, CTR, conversions, revenue |
| Review Cycle | Monthly optimization |
Pre-Send Checklist
Before every campaign:
-
Subject line optimized
-
Mobile preview tested
-
CTA clearly visible
-
Correct segment selected
-
Unsubscribe working
-
Tracking enabled
FAQs — Building an Email Marketing Plan
How often should I send emails?
Once a week or biweekly works well for most brands. Adjust based on engagement.
What’s a good open rate?
20–30% is a strong benchmark across most industries.
How many emails should be in a welcome series?
3–7 emails spread across 1–3 weeks.
Should every email sell something?
No. Value-driven emails should dominate over promotions.
When should I clean my email list?
Every 3–6 months.
Do I need advanced design for emails?
Simple designs often outperform heavy visual layouts.
Is email better than social media for sales?
Email typically converts higher because it targets owned audiences directly.
Conclusion — Why a Strategic Email Marketing Plan Wins Long-Term
Email marketing success doesn’t come from occasional blasts—it comes from structure, segmentation, automation, and performance optimization. Whether you’re running email marketing for small businesses, email marketing for restaurants, managing campaigns for tech firms, or driving traffic as a blogger, email remains one of your most reliable growth engines.
With the right plan, your emails stop being just messages—and start becoming predictable revenue and relationship drivers.